What is Circumvallete Placenta? | Pensacola Midwives
During pregnancy, the placenta plays a vital role in providing nutrients and oxygen to the growing fetus. However, complications can arise, and one such complication is a circumvallate placenta. This condition, though relatively rare, can pose risks to both the mother and the baby. In this article, we'll delve into what circumvallate placentas are, their causes, associated risks, and how they are managed.
What is a Circumvallate Placenta?
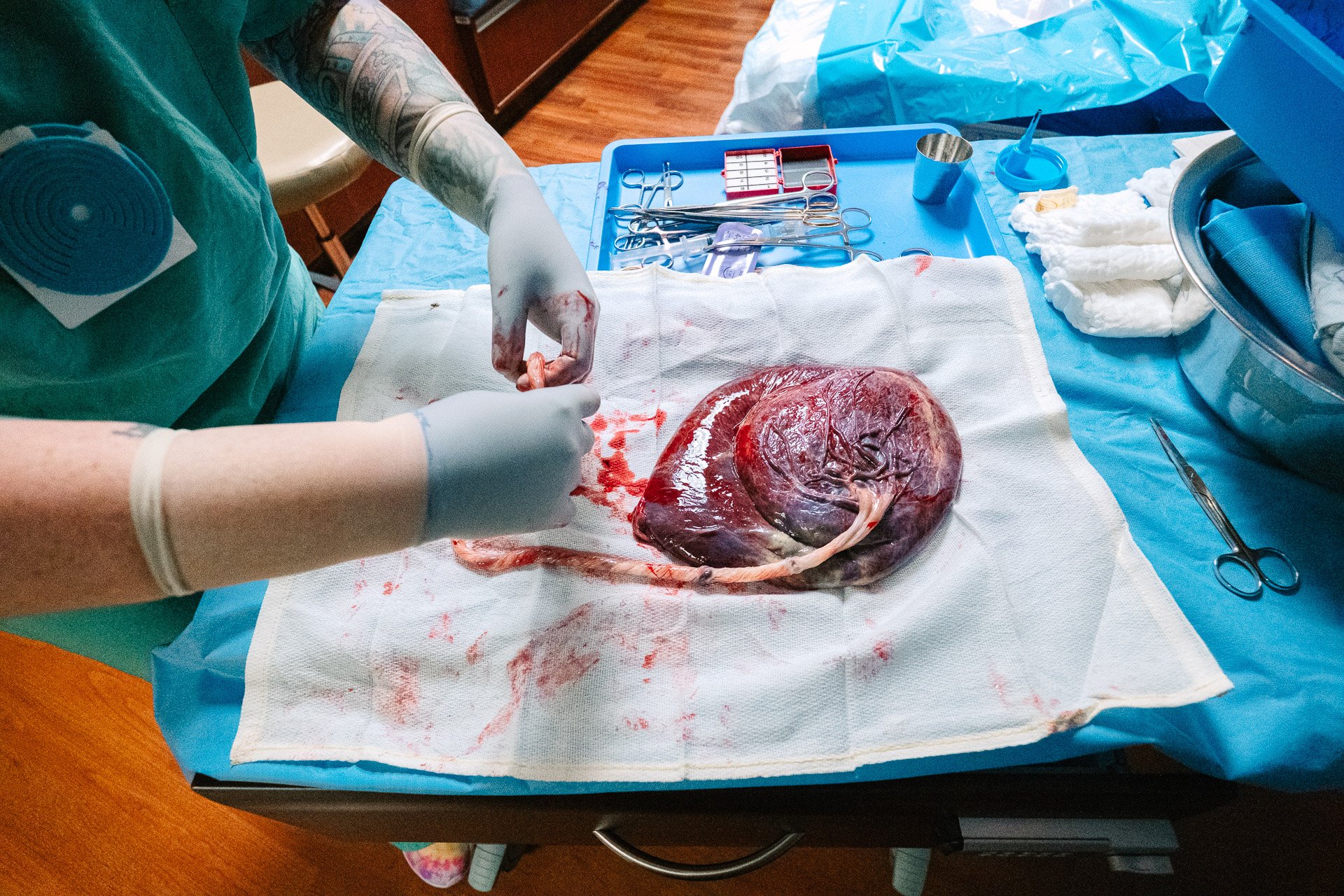
A circumvallate placenta is a structural abnormality where the placental margin forms a thickened ring around its edge. This ring-like structure can lead to several complications during pregnancy and childbirth. Normally, the placenta is disc-shaped with a smooth edge. However, in circumvallate placenta, the edge appears raised and folded inward, resembling a rolled-up rim.
What Causes Circumvallate Placenta?
The exact cause of circumvallate placenta formation is not fully understood. However, it is believed to be associated with abnormal implantation of the placenta in the uterus during early pregnancy. Factors such as uterine anomalies, previous cesarean sections, advanced maternal age, and certain medical conditions like hypertension may increase the risk of developing this condition.
Risks Associated with Circumvallate Placentas:
Placental Insufficiency: The thickened ring in a circumvallate placenta can impair blood flow to the fetus, leading to inadequate delivery of oxygen and nutrients. This can result in fetal growth restriction and other complications.
Preterm Birth: Women with circumvallate placentas are at an increased risk of preterm labor and delivery. The compromised placental function may trigger early onset of labor.
Placental Abruption: Circumvallate placentas are associated with a higher risk of placental abruption, where the placenta separates from the uterine wall before delivery. This can lead to severe bleeding and compromise fetal oxygenation.
Postpartum Hemorrhage: The abnormal placental structure may increase the risk of excessive bleeding after childbirth, necessitating prompt medical intervention.
Management and Treatment of Circumvallate Placenta
Managing a pregnancy complicated by a circumvallate placenta requires close monitoring and timely interventions to minimize risks to both the mother and the baby. Here are some key aspects of management:
Prenatal Monitoring: Regular prenatal visits with obstetricians are essential for monitoring fetal growth, assessing placental function, and detecting any complications early.
Ultrasound Evaluation: Ultrasound scans can help in diagnosing circumvallate placenta by visualizing the characteristic thickened ring at the placental margin. Serial ultrasounds may be performed to monitor fetal growth and amniotic fluid levels.
Fetal Surveillance: Non-stress tests (NSTs) and biophysical profile (BPP) tests may be recommended to assess fetal well-being and detect signs of distress.
Timing of Delivery: Depending on the severity of complications and gestational age, healthcare providers may recommend early delivery to prevent further fetal compromise. However, the decision regarding the timing of delivery should be individualized based on maternal and fetal factors.
Cesarean Section: In some cases, a cesarean section may be planned to minimize the risk of complications associated with vaginal delivery, such as placental abruption and postpartum hemorrhage.
In conclusion, while circumvallate placentas are relatively rare, they can have significant implications for pregnancy outcomes. Early detection, close monitoring, and appropriate management are crucial for optimizing maternal and fetal health. Expectant mothers with this condition should receive comprehensive care from a multidisciplinary team, including obstetricians, maternal-fetal medicine specialists, and neonatologists, to ensure the best possible outcomes for both mother and baby.